![]()
abess (Adaptive BEst Subset Selection) library aims to
solve the general best subset selection problem, i.e., find a small
subset of predictors such that the resulting model is expected to have
the highest accuracy. The selection for best subset shows great value in
scientific researches and practical application. For example, clinicians
wants to know whether a patient is health or not based on the expression
level of a few of important genes.
This library implements a generic algorithm framework to find the optimal solution in an extremely fast way. This framework now supports the detection of best subset under: linear regression, classification (binary or multi-class), counting-response modeling, censored-response modeling, multi-response modeling (multi-tasks learning), etc. It also supports the variants of best subset selection like group best subset selection, nuisance penalized regression, especially, the time complexity of the best (group) subset selection for linear regression is certifiably polynomial.
To install the abess R package from CRAN, just run:
install.packages("abess")Alternative, you can install the newest version of abess
by following this
instruction.
To show the power of abess in computation, we assess its
timings of the CPU execution (seconds) on synthetic datasets, and
compare to state-of-the-art variable selection methods. The variable
selection and estimation results are deferred to performance.
All computations are conducted on a Ubuntu platform with Intel(R)
Core(TM) i9-9940X CPU @ 3.30GHz and 48 RAM. We compare
abess R package with three widely used R packages:
glmnet, ncvreg, and L0Learn. We
get the runtime comparison results:
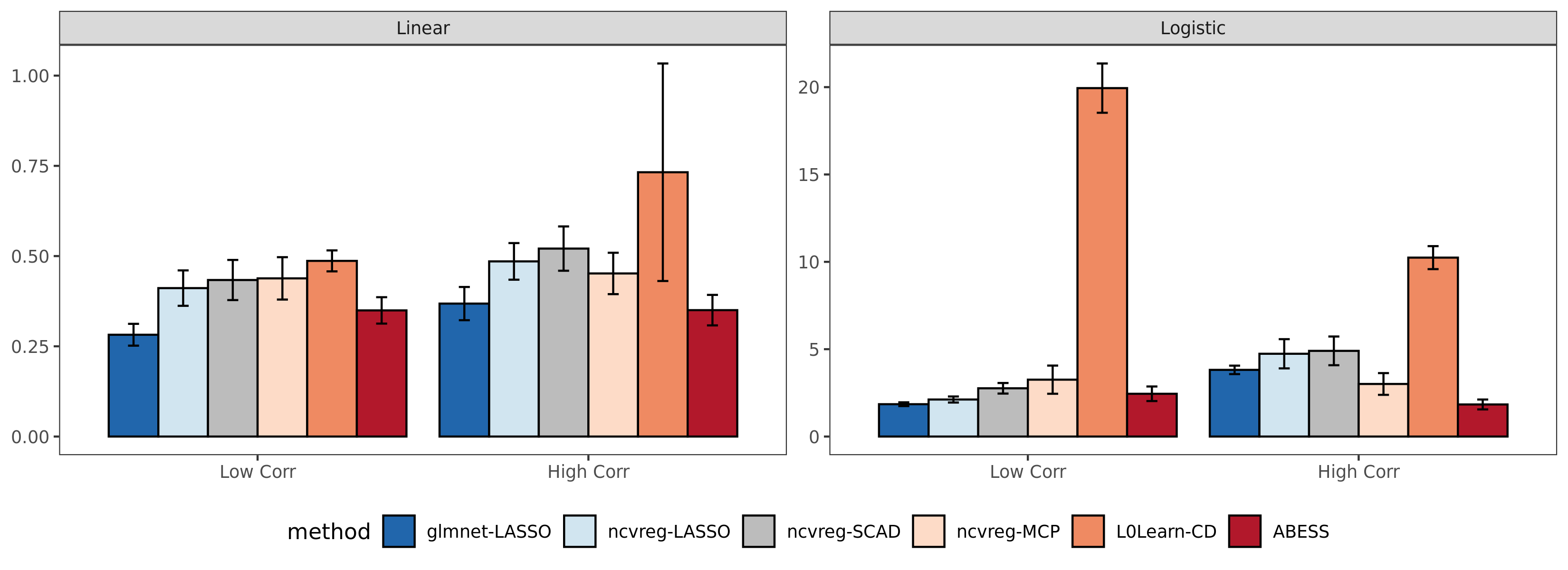
Compared with the other packages, abess shows
competitive computational efficiency, and achieves the best
computational power when variables have a large correlation.
Conducting the following command in shell can reproduce the above results in R:
$ Rscript abess/docs/simulation/R/timings.RNew features supported by the latest version (0.4.5):
Support generalized linear model for ordinal response (setting
family = "ordinal"), also named as rank learning in machine
learning community.
Support robust principal analysis
Modify R package structure to make many internal components are reusable.
If you use abess or refer to our tutorials in a
presentation or publication, we would appreciate citations of our
library.
Zhu Jin, Xueqin Wang, Liyuan Hu, Junhao Huang, Kangkang Jiang, Yanhang Zhang, Shiyun Lin, and Junxian Zhu. “abess: A Fast Best-Subset Selection Library in Python and R.” Journal of Machine Learning Research 23, no. 202 (2022): 1-7.
The corresponding BibteX entry:
@article{JMLR:v23:21-1060,
author = {Jin Zhu and Xueqin Wang and Liyuan Hu and Junhao Huang and Kangkang Jiang and Yanhang Zhang and Shiyun Lin and Junxian Zhu},
title = {abess: A Fast Best-Subset Selection Library in Python and R},
journal = {Journal of Machine Learning Research},
year = {2022},
volume = {23},
number = {202},
pages = {1--7},
url = {http://jmlr.org/papers/v23/21-1060.html}
}Junxian Zhu, Canhong Wen, Jin Zhu, Heping Zhang, and Xueqin Wang (2020). A polynomial algorithm for best-subset selection problem. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 117(52):33117-33123.
Zhu Jin, Xueqin Wang, Liyuan Hu, Junhao Huang, Kangkang Jiang, Yanhang Zhang, Shiyun Lin, and Junxian Zhu. “abess: A Fast Best-Subset Selection Library in Python and R.” Journal of Machine Learning Research 23, no. 202 (2022): 1-7.
Pölsterl, S (2020). scikit-survival: A Library for Time-to-Event Analysis Built on Top of scikit-learn. J. Mach. Learn. Res., 21(212), 1-6.
Yanhang Zhang, Junxian Zhu, Jin Zhu, and Xueqin Wang. A Splicing Approach to Best Subset of Groups Selection. INFORMS Journal on Computing (Accepted). doi:10.1287/ijoc.2022.1241.
Qiang Sun and Heping Zhang (2020). Targeted Inference Involving High-Dimensional Data Using Nuisance Penalized Regression, Journal of the American Statistical Association, DOI: 10.1080/01621459.2020.1737079.